stravanasu
- 11 Posts
- 66 Comments

 361·1 month ago
361·1 month ago“Ethical and legal objections”. The point in this case is that what’s legal is unethical, and what’s ethical is illegal. Analogous to other situations through history and countries, for example in the USA when it was illegal for black people to sit in certain parts of a bus, or in Germany when marriage with Jewish people was illegal.
As human beings, it’s always important to make the ethical choice.

 7·2 months ago
7·2 months ago“Science of the Total Environment” journal? 🤣🤣🤣🤣🤣 Too silly even for a 3rd-rate sci-fi film…

 11·3 months ago
11·3 months agothese autonomous agents represent the next step in the evolution of large language models (LLMs), seamlessly integrating into business processes to handle functions such as responding to customer inquiries, identifying sales leads, and managing inventory.
I really want to see what happens. It seems to me these “agents” are still useless in handling tasks like customer inquiries. Hopefully customers will get tired and switch to companies that employ competent humans instead…

 2·3 months ago
2·3 months ago😂

 18·3 months ago
18·3 months agoThe current security philosophy almost seems to be: “In order to make it secure, make it difficult to use”. This is why I propose to go a step further: “In order to make it secure, just don’t make it”. The safest account is the one that doesn’t exist or that can’t be accessed by anyone, including its owner.

 2·3 months ago
2·3 months agoWe aren’t supposed to accept that. We can simply not use their software. And as users that’s the only power we have on devs. But it’s a power that only works on devs who are interested in having many users.

 9·3 months ago
9·3 months agoNobel prize in computer science. Looks like the Nobel Prize committee has forgotten what Physics is.

 2·4 months ago
2·4 months agoFully agree.
It’s worth posting the blog post you linked.

 11·1 year ago
11·1 year agoAs most who have already commented here, I’m somewhat unimpressed (and would expect more analytical subtlety from a scientist). Wittgenstein already fully dissected the notion of “free will”, showing its semantic variety of meanings and how at some depth it becomes vague and unclear. And Nietzsche discussed why “punishment” is necessary and makes sense even in a completely deterministic world… Sad that such insights are forgotten by many scientists. Often unclear if some scientists want to deepen our understanding of things, or just want sensationalism. Maybe a bit of both…

 7·1 year ago
7·1 year agoAgree (you made me think of the famous face on Mars). I mean that more as a joke. Also there’s no clear threshold or divide on one side of which we can speak of “human intelligence”. There’s a whole range from impairing disabilities to Einstein and Euler – if it really makes sense to use a linear 1D scale, which very probably doesn’t.

 64·1 year ago
64·1 year agoTitle:
ChatGPT broke the Turing test
Content:
Other researchers agree that GPT-4 and other LLMs would probably now pass the popular conception of the Turing test. […]
researchers […] reported that more than 1.5 million people had played their online game based on the Turing test. Players were assigned to chat for two minutes, either to another player or to an LLM-powered bot that the researchers had prompted to behave like a person. The players correctly identified bots just 60% of the time
Complete contradiction. Trash Nature, it’s become only an extremely expensive gossip science magazine.
PS: The Turing test involves comparing a bot with a human (not knowing which is which). So if more and more bots pass the test, this can be the result either of an increase in the bots’ Artificial Intelligence, or of an increase in humans’ Natural Stupidity.

 5·1 year ago
5·1 year agoThis is so cool! Not just the font but the whole process and study. Please feel free to cross-post to Typography & fonts.

 2·1 year ago
2·1 year agodealt untold damage onto the collective psyche
Couldn’t think of a better way to put it!!

 4·1 year ago
4·1 year agoFantastic, thank you!

 7·1 year ago
7·1 year agoAbsolutely amazing!! I suppose you’ve seen some renderings like this one.
However, these molecules don’t really have a will or a scope, and in fact I don’t like how they are deceivingly represented in some of these animations. These animations show, say, some aminoacid that goes almost straight towards some large molecule and does this and that. And one is left with the question: how does it get there and how does it “know” that it should get there? The answer is that it’s just immersed in water and moved about by the unsystematic motion of the water molecules. Some aminoacids go here, some go there. In these animations they only show the ones that end up connecting with the large molecule. OK, this is done just to simplify the visualization, but it can also be misleading.
Similarly with molecules like kinesin, which seem to purposely walk around. Also in that case there’s a lot of unsystematic motion, that after a while ends in a particular more stable configuration thanks to electromagnetic forces. Simulations such as this or this give a more realistic picture of these processes.
Don’t get me wrong, I’m not saying that the whole thing isn’t awe-inspiring or mind blowing. It is. Actually I think that the more realistic picture (without these “purposeful” motions) leads to even more awe, because of the structured complexity that comes out of these unsystematic motions.

 16·1 year ago
16·1 year agoWhen I used to run simulations, a current of the size of the Gulf Stream could be turned on (with winds and Earth’s rotation), from nothing, in around 400 years (see p. 68). Then it maintained steadily. But turning off or changing in important ways can happen much faster. I’d like to know as well. There should be open-access articles in that journal about this.
You’re simplifying the situation and dynamics of science too much.
If you submit or share a work that contains a logical or experimental error – it says “2+2=5” somewhere – then yes, your work is not accepted, it’s wrong, and you should discard it too.
But many works have no (visible) logical flaws and present hypotheses within current experimental errors. They explore or propose, or start from, alternative theses. They may be pursued and considered by a minority, even a very small one, while the majority pursues something else. But this doesn’t make them “rejected”. In fact, theories followed by minorities periodically have breakthroughs and suddenly win the majority. This is a vital part of scientific progress. Except in the “2+2=5” case, it’s a matter of majority/minority, but that does emphatically not mean acceptance/rejection.
On top of that, the relationship between “truth” and “majority” is even more fascinatingly complex. Let me give you an example.
Probably (this is just statistics from personal experience) the vast majority of physicists would tell you that “energy is conserved”. A physicist specialized in general relativity, however, would point out that there’s a difference between a conserved quantity (somewhat like a fluid) and a balanced quantity. And energy strictly speaking is balanced, not conserved. This fact, however, creates no tension: if you have a simple conversation – 30 min or a couple hours – with a physicist who stated that “energy is conserved”, and you explain the precise difference, show the equations, examine references together etc, that physicist will understand the clarification and simply agree; no biggie. In situations where that physicist works, this results in little practical difference (but obviously there are situations where the difference is important.)
A guided tour through general relativity (see this discussion by Baez as a starting point, for example) will also convince a physicist who still insisted that energy is conserved even after the balance vs conservation difference was clarified. With energy, either “conservation” makes no sense, or if we want to force a sense, then it’s false. (I myself have been on both sides of this dialogue.)
This shows a paradoxical situation: the majority may state something that’s actually not true – but the majority itself would simply agree with this, if given the chance! This paradoxical discrepancy arises especially today owing to specialization and too little or too slow osmosis among the different specialities, plus excessive simplification in postgraduate education (they present approximate facts as exact). Large groups maintain some statements as facts simply because the more correct point of view is too slow to spread through their community. The energy claim is one example, there are others (thermodynamics and quantum theory have plenty). I think every physicist working in a specialized field is aware about a couple of such majority-vs-truth discrepancies. And this teaches humbleness, openness to reviewing one’s beliefs, and reliance on logic, not “majorities”.
Edit: a beautiful book by O’Connor & Weatherall, The Misinformation Age: How False Beliefs Spread, discusses this phenomenon and models of this phenomenon.
Peer review, as the name says, is review, not “acceptance”. At least in principle, its goal is to help you check whether the logic behind your analysis is sound and your experiments have no flaws. That’s why one can find articles with completely antithetical results or theses, both peer-reviewed (and I’m not speaking of purchased pseudo peer-review). Unfortunately it has also become a misused political or business tool, that’s for sure – see “impact factors”, “h-indexes”, and similar bulls**t.


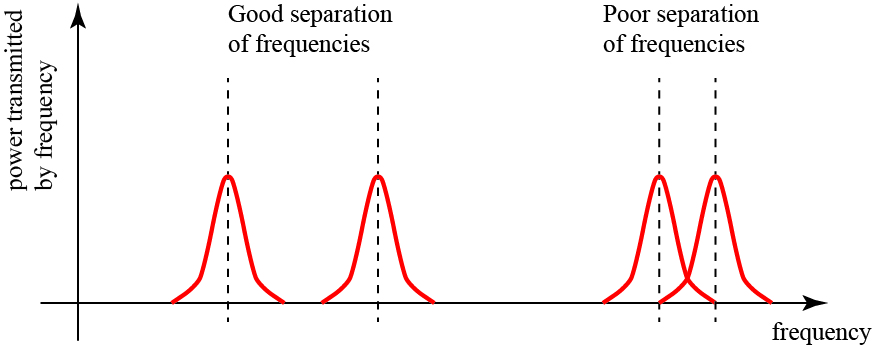
Restored! Maybe worth a post update?