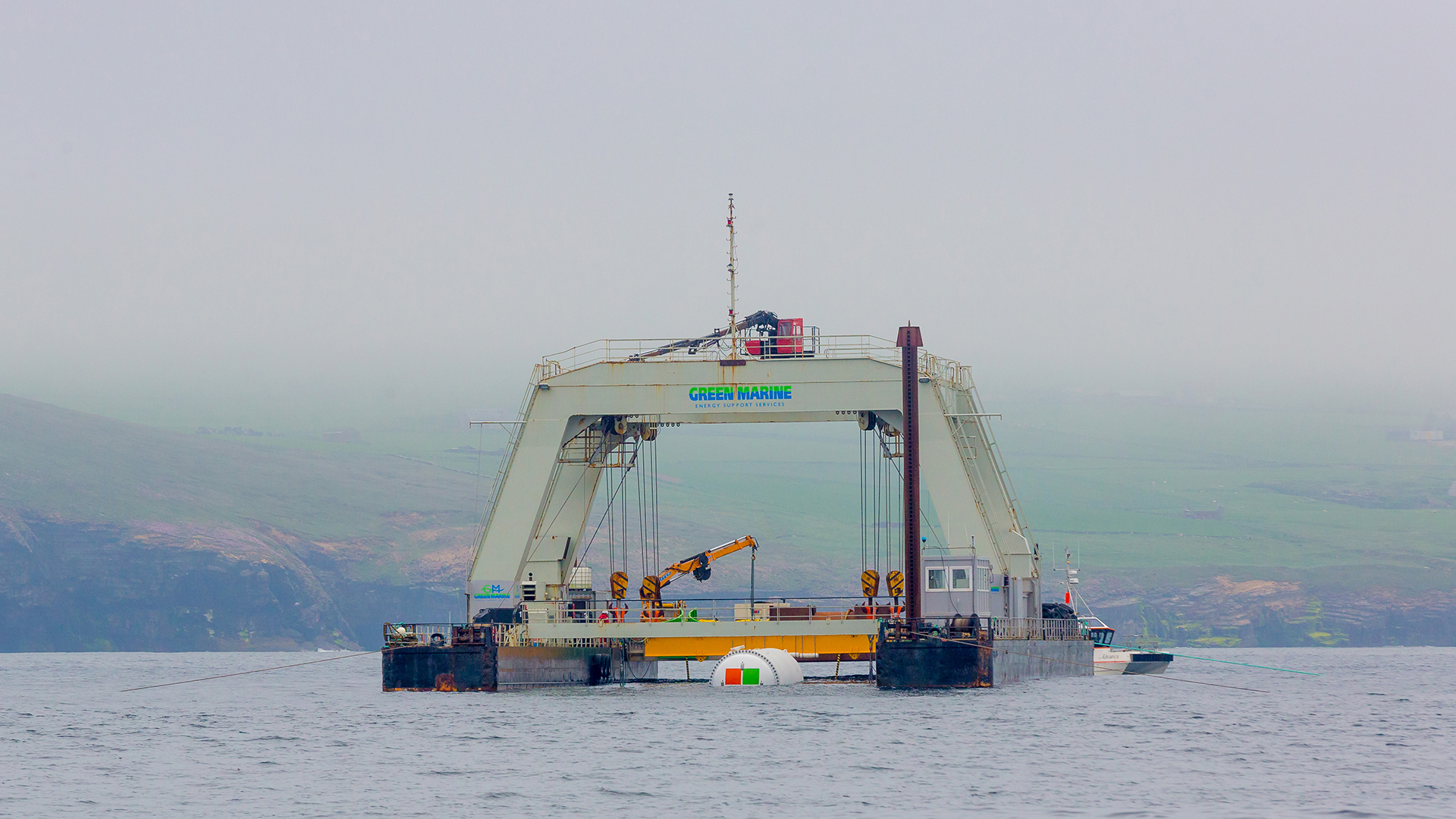
Microsoft are looking at putting datacenters under the ocean, which sounds like a really good idea to cool them but I can’t help but think a couple decades from now it’s going to start causing us problems
Well it’s certainly better environmentally than using conventional air conditioning, doubt it would heat up the oceans significantly
Would it heat up the oceans: yes.
Significantly:no.
If this pans out it would be a lot better than what we are doing now.
It will always be less heating than if you use aircon.
There was this quote they gave when asked about impact to the surrounding ocean.
Natick uses raw sea water for cooling, with the water returned to the ocean a fraction of a degree warmer than ambient. Due to rapid mixing in ocean currents, the temperature impact just a few meters downstream of the datacenter is undetectable. We used cameras on the exterior of the vessel to observe wildlife during deployment. We found that the datacenter provided an attractive location for sea life, and was quickly colonized by multiple species of fish and other sea life.At a huge scale, that maybe could be an issue if you extrapolate. But as others have pointed out, data centers today already require air and water cooling which isn’t likely as efficient so net gain on the environment is probably worse with land data centers in terms of cooling. And they noted the hardware inside had a higher reliability, potentially due to its pure nitrogen atmosphere in the capsule, so that’s less need for buying replacement servers and performing maintenance.
No clue if this thing is actually feasible beyond small scale due to the very high deploy and retrieval costs. But in my opinion this isn’t like some environmentally oblivious solution.
I would imagine it might actually work out cheaper to deploy no? No need to build buildings for these data centers, no need to pay for the land they are built on and no need to spend money powering a shit ton of cooling
At the limit, it could depend on the extent to which adding heat to the ocean has different/worse effects than adding it to the atmosphere. E.g. maybe ocean heat is worse for wildlife or disrupts currents or doesn’t radiate away into space as fast, or something like that.
Definitely not a problem to worry about in the short-term, of course. But then again, the same was said about lots of other problems back in the day that we do have to worry about now, so…
Would you kindly swap out the memory on that server?
The container is regarded as a single unit; if a server inside the container fails the functions of that server are offloaded to another available server and it is taken out of service.
Once enough servers in a container are offline the entire unit has all computational load offloaded to another, identical container with sufficient capacity.
Then the now-offline unit is retrieved and serviced; probably a ground-up rebuild of all components.
… but I do like the idea of some dude in a wetsuit trying to replace a memory stick.
Yeah that’s totally more environmently friendly to chuck hardware to the mercy of salt water… What could go wrong there??
The salt water won’t come into contact with anything except pumps, a heat exchanger and the exterior of the container.
The servers live in a nitrogen environment, so it reduces corrosion, I doubt there would be any dirt or dust. It’s going to be an incredible sterile environment.
No one does maintenance on the server farms. It costs more money to send someone in than to let the parts slowly die until the farm no longer is economically viable. Once that happens, you sell the whole farm to a recycler.
That sounds monumentally more wasteful.
But it is cheaper.
The most sustainable option would also always be the cheapest option, if regulations were properly designed to correct for externalized costs. We should strive for that.
I can tell you that big data centers likely have a 4 year hardware cycle, where it is all under warranty and service contract.
After which, it gets sold to refurbishers who refurb it and resell it. Or the datacenter may repurpose it for labs, OOB hardware, or donate it to schools.A lot of smaller companies don’t need the latest and greatest, and are quite happy running old 2nd hand hardware.
Even after they are done with it, there are plenty of hobbyists that will buy it. I have a couple 8 year old servers that run absolutely fine for what I need.
Old servers are also kept around as parts for companies that refuse to update old hardware (and will just keep buying spares, or like-for-like replacements).
The last step is ewaste, where the good stuff gets boiled in acid to extract the gold, or whatever they do.The only things that are generally destroyed during hardware cycles are the storage, and that’s normally for compliance reasons.
It might be the most sustainable option.
Building a server farm that needs to be maintained means building out space for people to maintain the farm, increasing the space and requiring additional cooling to make the farm able to be serviced by humans.
It also means that less efficient hardware gets used for a longer period of time, driving up electricity costs.
And as long as the e-waste is recycled, in which it is easier to recycle an entire farm rather than consumer electronics, what is the issue?
For microsoft at the expense of the fucking planet.
This is common practice for any large data center.
No it isn’t. What DC do you work at? We recycle hardware as much as fucking possible until its worthless and then it’s sold to anyone who wants it in the company first and then the rest is sold on ebay and craigslist.
Ahhh, so this is why you are so angry in this thread. You’re the competition. Not exactly an unbiased third party.
What’s the difference between recycling one piece at a time or en mass?
One hasn’t been corroded by the ocean.
The actual computer parts wouldn’t necessarily be corroded though, I would assume the hull itsself would be designed to last longer than the computer components themselves
Yes we all know that designs are always perfect and never stupid or wasteful for greenwashing and marketing.
Same for wind, solar, geothermal, nuclear energy generation then?
I mean not really because the computers in the farm at this point are recycled to be sold as seperate used units.
Microsoft’s next invention will be a Memory Swap plasmid lol
I understood that reference…
finally…thank you.
It would take quite a bit of energy to effect things on a global scale but it could cause some issues at a very local level.
As is usual with renewable energy sources
Considering all the volcanoes and heat vents down there, I doubt a data center is going to tip any scales.
Realistically probably not and as people have pointed out it’s better than them doing it into the air less efficiently but my point was not about a single data center it was more if it caught on and we started dumping thousands of these things in the ocean
If we moved all data center cooling into the ocean, we would likely reduce the rate of ocean warming from burning fossil fuels (creating heat and CO2) used to power a data center that uses ~40% (on average) of its energy to cool the data center rather than for compute.
Not really. It’s not like there’s a nuke reactor in there.
There isn’t a nuke reactor in there, is there?
Now you’re talkin!
At the deployment site, a remotely operated vehicle retrieved a cable containing the fiber optic and power wiring from the seafloor and brought it to the surface where it was checked and attached to the datacenter, and the datacenter powered on.
Sadly, it sounds like power is coming from the shore.
Underwater datacenters could also serve as anchor tenants for marine renewable energy such as offshore wind farms or banks of tidal turbines, allowing the two industries to evolve in lockstep.
But I think this is their plan for energy in the future.
Onshore, wind turbines sprout from farmers’ rolling fields and solar panels adorn roofs of centuries-old homes, generating more than enough electricity to supply the islands’ 10,000 residents with 100 percent renewable energy. A cable from the Orkney Island grid sends electricity to the datacenter, which requires just under a quarter of a megawatt of power when operating at full capacity.
It’s still pretty darn clean.
It’s not clean at all. You’re burying disposable hardware into extremely corrosive salt water and then throwing away the whole thing when it fails. What the fuck is green about that?
All hardware is “disposable” in the sense that it becomes obsolete after a few years, and the electricity to keep using it costs more than replacing it with new hardware with better performance per watt.
Maybe once Moore’s law is finally dead and buried that’ll stop being the case, but it hasn’t happened quite yet.
This certainly isn’t “green” in terms of disposal, but I’m not sure it’s any worse than the status quo alternative of a landfill, either.
But we recycle e-waste. You’re not recycling shit that’s been corroded by the ocean. It’s ruined, not just obsolete. We already have fully-renewable data-centers. This just makes more problems than it solves which is why there’s been no update to this article from 2018.
But we recycle e-waste.
Oh you sweet, summer child.
The thought of these plus tidal generators makes my day.
Yeah, the Orkney Islands are also experimenting with tidal generators (Wikipedia/European Marine Energy Centre), though the weather there is ideal for wind energy.
I can’t wait to reserve some compute time for when the ocean data center is getting wind power.
Considering the sheer volume of wasted space, power and cooling going into these behemoth machine learning data centres today, I think the net benefit of this would be overwhelmingly positive.
Why would this be a bad thing? Doubt it happens at any scale but this seems like a perfectly viable way to cool data centers compared to how energy intensive they are today.
I imagine people are concerned about disposal and failures. They are unmaintainable ewaste containers
But without oxygen and with fewer vibrations from cooling, they last 5years longer with no maintenance.
Do you know what salt water does to literally almost any man made materials?
I’m sure the engineers who made this know. And if they didn’t, this is an article from 2018, they would have most certainly found out by now.
Which makes you wonder why there’s no update because this is something that we’ve known about for thousands of years and still need to constantly repaint boats because the ocean doesn’t give a fuck.
Maybe they’re able to use different materials? After all boats need to float so maybe they need to use lighter, less durable materials and have thinner walls
These things could be made as dense and thick as needed because they explicitly need not to float
My understanding is that they take a data center rack, stick it in a metal tube, then replace all the oxygen with an inert gas like argon, then sink to the bottom of the ocean. I think seawater is only exposed to the outside low tech metal.
Right but you’ve got to remember that these are off the shelf computers so they need cabling and wires, fans, all manner of drives that will fail, connections to the outside. Are they cooling the CPUs with saltwater or just the cooling equipment? Because either way is either risky via corrosion or just as inefficient, now with the added complication of having everything at the mercy of N, underwater.
Again, this whole thing just screams like greenwashing horseshit and the fact that there’s been no update for half a decade leads me to believe that the project was a failure.
Ehh, it could sound that way (green washing). I remember an article from 1 or 2 years ago where Microsoft did a “pilot” test of this and the general consensus is that in a datacenter
- while you fix part a you break part b of the identical server next to it.
- Moore’s law means that every 5 years or so you spend more on electricity and storage than you would for the smaller more efficient hardware
- having 0 human interaction and 0 added dust and 0 oxygen and the ocean at 40 decrees farenheight meant that no additional cooling required. (Maybe some cpu airflow to the external 40° air)
Time (and investments) will tell if this is the solution to costly land based air heat pumps to cool datacenters with human interactions.
im way more worried about undersea mining than i am data centers being underwater.
I like the idea of using renewable energy (tidal, wind) right where it’s produced.
It’s apparently the demonstration phase and for now rely on an power coming from elsewhere. Once it’s deploy I hope they keep their promise to rely on local energy production.
I wonder if they’d allow it to be a bit of an artificial reef… I’d like that concept.
I doubt they’d be able to stop it from becoming one, especially if they don’t want to spend the server downtime to haul it out for repainting.
It’s just greenwashing, just a concept that was mothballed ten minutes after the photo op
Well, you are right that Microsoft never applied this large-scale, nor does it currently run any underwater datacenters. But project Natick anyway ran for over five years, with the first prototype having been deployed in 2015 and the last one recovered in 2020. So apparently not exactly the definitive future of Microsoft datacenters, but much more than a photo op.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_Natick
https://natick.research.microsoft.com/
https://news.microsoft.com/source/features/sustainability/project-natick-underwater-datacenter/
The system pipes seawater directly through the radiators on the back of each of the 12 server racks and back out into the ocean.
How much is it going to heat the local area? Along with disk and rack design testing, are they also testing how this thing affects wildlife?
The appeal is understandable: proximity to population centers, temperature, security, scaling with renewable tech, etc.
I wonder if international waters is their end goal. Self-reliant, off-grid data centers that only abide by MS rules.
Everything has to be cooled, it’s a question of efficiency. Directly exchanging the heat into cold water is arguably better than expending fossil fuels to generate electricity to pump the heat out of your servers and into the atmosphere. You get multiple losses with current technology: fossil fuel efficiency losses, electric line losses, air conditioning efficiency losses. And the additional electrical generation dumps more CO2.
Oh no doubt. It makes a great deal of sense.
I’m just curious what the actual heat output is (avg, min, max, in vs out), and what the environmental impact is.
Will there be biofouling because the warm seawater is desirable?
Will it even be viable offshore from places like Miami?
Can it produce too much heat for the local environment? Probably not one, but what about after this scale-up with renewables like the article mentions?
At what scale would it begin to disrupt things like the AMOC?
I wonder if international waters is their end goal. Self-reliant, off-grid data centers that only abide by MS rules.
Reduction of power requirements.
https://dataspan.com/blog/how-much-energy-do-data-centers-use/
For many data centers, the cooling system is one of the most energy-intensive components in the facility. The average data center cooling system consumes about 40% of the center’s total power.
Further reading:
- https://www.nrel.gov/computational-science/measuring-efficiency-pue.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_usage_effectiveness
From nrel.gov (National Renewable Energy Lab) site:
When the Energy Systems Integration Facility (ESIF) was conceived, NREL set an aggressive requirement that its data center achieve an annualized average power usage effectiveness (PUE) of 1.06 or better. Since the facility opened, this goal has been met every year—and the data center has now achieved an annualized PUE rating of 1.036.
Studies show a wide range of PUE values for data centers, but the overall average tends to be around 1.8. Data centers focusing on efficiency typically achieve PUE values of 1.2 or less. PUE is the ratio of the total amount of power used by a computer data center facility to the power delivered to computing equipment.
(I wanna say that 1.036 for PUE is amazing - but all the stuff they did to get there is expensive)
So how do they deal with the salty ocean water corroding everything? I mean for cooling, they have to exchange heat with it somehow. Looking at pictures of wrecks, any kind of heat exchanger would likely rust or become covered in various lifeforms rather quickly.
I would imagine they can get away with using much heavier, stronger and thicker materials as these things have zero requirement for buoyancy or portability (besides getting them there in the first place)
Not sure how they’d prevent it from being covered in algae and they even mentioned that they noticed sealife was using it as a home
I reckon it’d be a combination of using the hull itsself as a giant heat sync and the fact they can get some pretty ridiculous cooling from the ocean to compensate for some inefficiency with heat transfer
Just my guess though
I don’t know why but hearing “moonshot” makes me cringe.